
Paleo Pals
Hello my name is Homo sapiens neanderthalensis!
...But you can call me a Neanderthal
Homo sapiens neanderthalensis also known as Neanderthals were first discovered in Germany in the mid-late 1800's in a limestone cave.
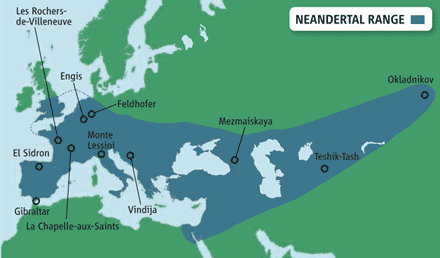
Neanderthals were found in Europe and middle east.
Neanderthals are our closest extinct human relative!
Neanderthals ranged across most of Europe and through the Middle East and central Asia. The first finding of me had people perplexed. Turns out i was their distant ancestor!


This is what i looked like compared to a modern human on the right.

Burial:
There is evidence that we deliberately buried our dead and occasionally even marked their graves with offerings, such as flowers. No other primates, and no earlier human species, had ever practiced this sophisticated and symbolic behavior!
Chapelle-aux-Saints was a neanderthal that was injured by an animal, causing the lost of his wrist and hand, a shorter leg, and had parts of his eye socket, nose, and jaw taken out.
This neanderthal actually survived because of evidence of these wounds healing over. He lived for quite some time after this.
Discoveries of elderly or deformed Neanderthal skeletons suggest that they took care of their sick and those who could not care for themselves. Neanderthals typically lived to be about 30 years old, though some lived longer.
We ate both meat and plants! We needed a good diet to help grow our brains and bodies.
We had kill sites, which is evidence that we hunted our food instead of scavenging.
THE BODY:
Some defining features of their skulls include the large middle part of the face, angled cheek bones, and a huge nose for humidifying and warming cold, dry air. Their bodies were shorter and stockier than ours, another adaptation to living in cold environments. But their brains were just as large as ours and often larger,1500-1750 cc - proportional to their brawnier bodies. From the neck down we looked like modern humans!
The first thought from scientist was that i was primitive, with bad posture and heavy bodies. When actually that was my bodies adaptation to the cold climate in Europe! A short and stocky body helped to retain heat.

This is what many artist thought we looked like just from looking at our bones and creating reconstructions of us! Many were believed to be red heads with light skin and blue eyes!

Neanderthals made and used a diverse set of sophisticated tools, controlled fire, lived in shelters, made and wore clothing, were skilled hunters of large animals and also ate plant foods, and occasionally made symbolic or ornamental objects.

We used stone tools similar to the ones used by other early humans, including blades and scrapers made from stone flakes. As time went on, they created tools of greater complexity, utilizing materials like bones and antlers. We used hand-axes, scrapers and blades as tools
How many tools can you see? Can you guess what they were used for?
Fire
We were the first to use fire with a purpose. We started fires by striking flint with hard minerals like pyrite to generate a spark. We could use fire to cook our food, provide light inside caves, protection and warmth in the cold climate.
How many Neanderthals do you see using fire in the painting?

We often took shelter from the ice, snow and otherwise unpleasant weather in Eurasia's plentiful limestone caves.
Many of our fossils have been found in caves, leading to the popular idea of them as "cave men."

It is believed that we wore clothes from animal skin and fur to protect us from the cold climate.
We wore fitted clothing, behaviors that would have greatly increased our chances of surviving the decreasing temperatures with the onset of ice ages.

Our Extinction:
No one knows exactly why we went extinct and why Homo sapiens survived.
Their presence may have prevented Neanderthals from expanding back into areas they once favored and served as a catalyst for the Neanderthal’s impending extinction.
Over just a few thousand years after modern humans moved into Europe, Neanderthal numbers dwindled to the point of extinction. All traces of Neanderthals disappeared by about 40,000 years ago.
The most recently dated Neanderthal fossils come from Western Europe, which was likely where the last population of this early human species existed.
Some scholars theorize that gradual or dramatic climate change led them to their demise, while others blame dietary deficiencies.
Another hypothesis is that Neanderthals didn't go extinct but simply interbred with humans until they were absorbed into our species was popular.

Can you see anything similar between us?
References:
Live Science: https://www.livescience.com/28036-neanderthals-facts-about-our-extinct-human-relatives.html
Ask a Biologist: https://askabiologist.asu.edu/plosable/proof-poop-what-neanderthals-ate
National Geographic: https://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2013/12/131216-la-chapelle-neanderthal-burials-graves/
Bright Hub: https://www.brighthubeducation.com/history-homework-help/117937-stone-tools-of-the-neanderthals/
History: https://www.history.com/news/neanderthals-fire-evidence-archaeology
Human Origins: http://humanorigins.si.edu/evidence/human-fossils/species/homo-neanderthalensis